
Healthy Gums, Healthy Smile
Expert Periodontics at Redwood Dental
Your gums are the foundation of your smile, and maintaining their health is essential for your overall well-being. At Redwood Dental, we offer comprehensive periodontal treatment to combat gum disease, treat gum recession, and help your gums remain strong and healthy. Whether you are dealing with early signs of gum disease or need advanced periodontal therapy, our expert team is here to provide personalized, compassionate care.
Understanding the Foundation of Gum Health
Periodontics is a specialized branch of dentistry that focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of periodontal (gum) disease, as well as the supporting structures of the teeth. This includes the gums, bone, and connective tissue that support your teeth. Periodontal disease is a common condition that can lead to serious oral health issues if left untreated.
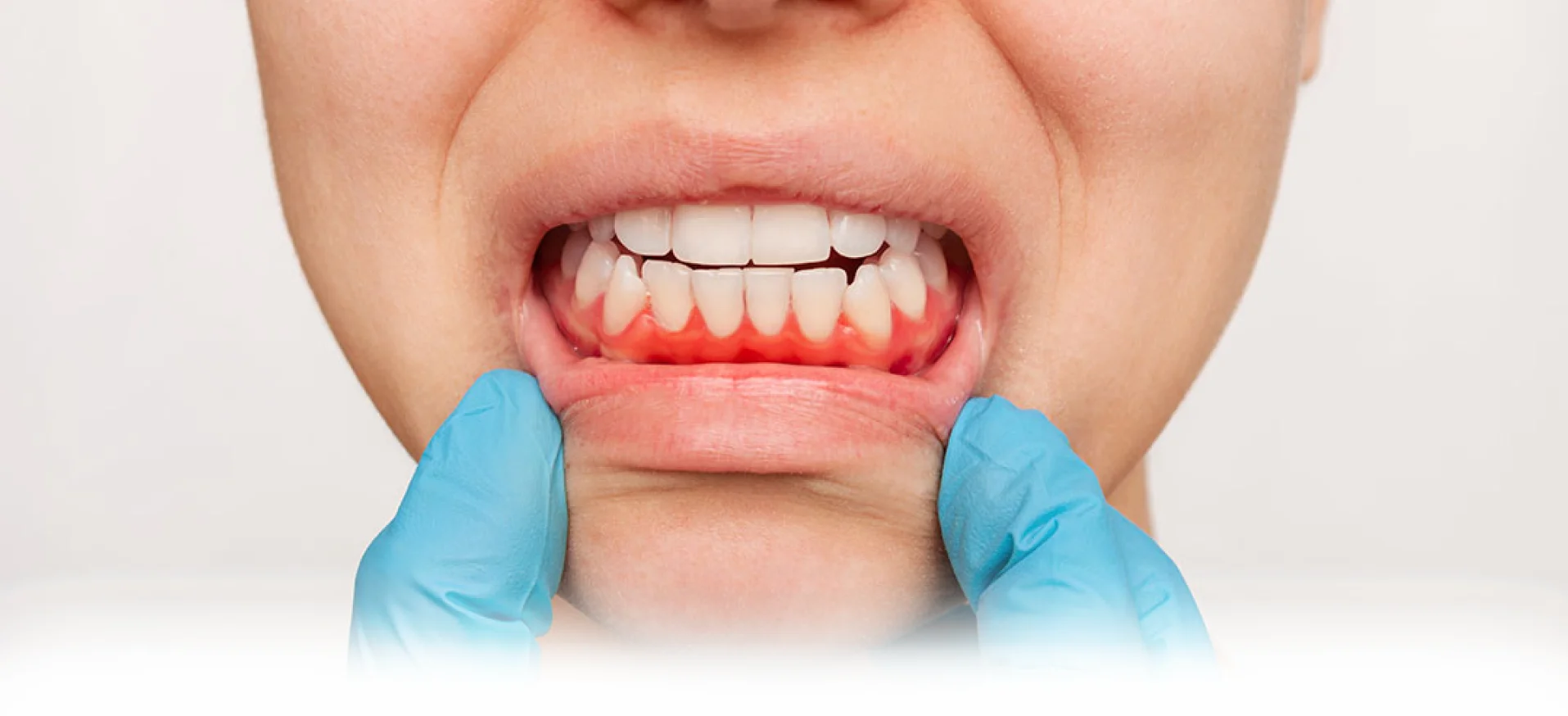
Recognizing Periodontal Disease Symptoms
Identifying the periodontal disease symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment. Some common signs to watch for include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums during brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums or teeth that appear longer than usual
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Changes in your bite or how your teeth fit together
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek professional care promptly to prevent further complications.
Comprehensive Periodontal Services at Redwood Dental
At Redwood Dental, we provide a full range of periodontal care to address gum health at every stage.
Periodontal Therapy for Gum Disease
Our tailored periodontal therapy options target the root causes of gum disease, restoring your oral health through deep cleaning, medication, and personalized care plans.
Gum Infection Treatment
Infections in the gums require prompt attention to prevent further damage. Our expert team identifies and treats gum infections with precision, relieving pain and promoting healing.
Treatment for Gum Recession
Receding gums expose the roots of your teeth, increasing sensitivity and the risk of decay. We offer innovative solutions like soft tissue grafting to restore gum tissue and protect teeth.
Periodontal Surgery
For advanced cases, periodontal surgery may be necessary. This includes pocket reduction surgery, regeneration techniques, and other procedures to restore gum and bone health.
Periodontal Maintenance
Ongoing care is crucial for maintaining healthy gums after treatment. Our periodontal maintenance program includes regular cleanings and monitoring to prevent the recurrence of gum disease.

Keeping Your Gums Healthy
After completing your initial treatment, ongoing periodontal maintenance is crucial for improving gum health. Regular visits to our office will help monitor your progress and make sure that any potential issues are addressed promptly.
Why Periodontal Health Matters?
Gum health affects more than just your smile, it is a crucial part of your overall health. Untreated gum disease can lead to:
- Advanced gum disease damages the tissue and bone that support your teeth.
- Gum infections are linked to heart disease, diabetes, and other health issues.
- Inflammation and sensitivity can interfere with daily activities like eating and speaking.
With proactive periodontic treatment, you can avoid these complications and enjoy a healthier life.
Why Do Patients Trust Our Periodontic Treatment?
Beyond Treatment: Support for Long-Term Gum Health
Maintaining your results after periodontal treatment requires consistent care. Our team will work with you to create a personalized maintenance plan, including:
- Regular cleanings and check-ups.
- At-home hygiene tips to optimize your oral care routine.
- Periodic evaluations to monitor your gum health and catch potential issues early.
Results That Speak for Themselves
The ultimate goal of periodontal care is to improve not just your gum health but your overall quality of life. At Redwood Dental, we take pride in helping our patients achieve life-changing results.
- Stronger, healthier gums that protect your teeth and oral health.
- Improved confidence from a beautiful, natural-looking smile.
- Relief from discomfort and pain caused by gum disease or recession.
- A healthier lifestyle with reduced risk of systemic health issues linked to gum disease.
Our success stories speak to the dedication and skill of our team, making Redwood Dental a trusted name in perio care for gum disease in Napa.
Make an Appointment
(707) 255-5100
Stages of Gum Disease: Early Detection Saves Smiles
Gum disease progresses in stages, each requiring a unique approach to treatment:
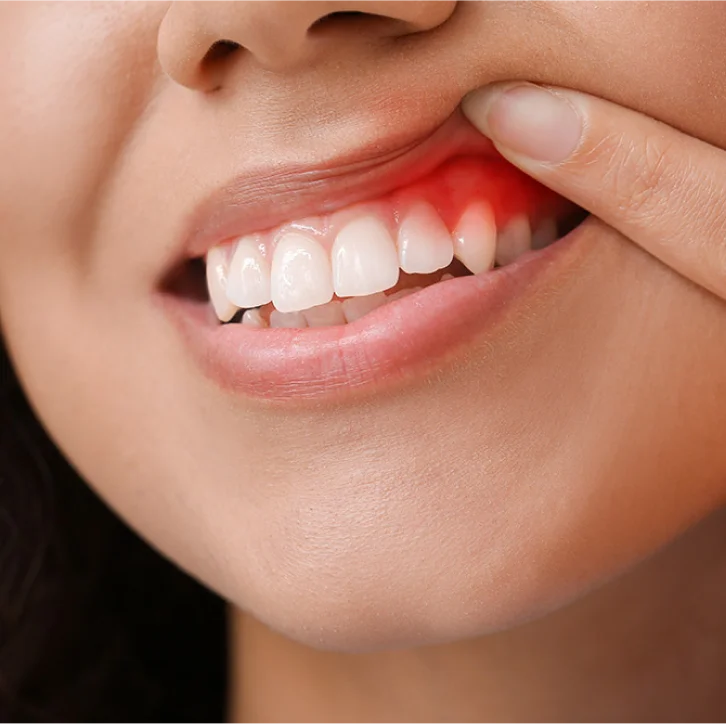

Redwood Dental: Your Partner in Periodontal Health
We understand that gum health impacts more than just your teeth. It affects your well-being and confidence. That is why Redwood Dental is committed to delivering the highest standard of periodontal care in Napa, tailored to your unique needs.
Call us today to schedule your consultation and discover why we’re the best periodontist for gum disease in Napa.
Contact Us
